What Is 20/20 vision?
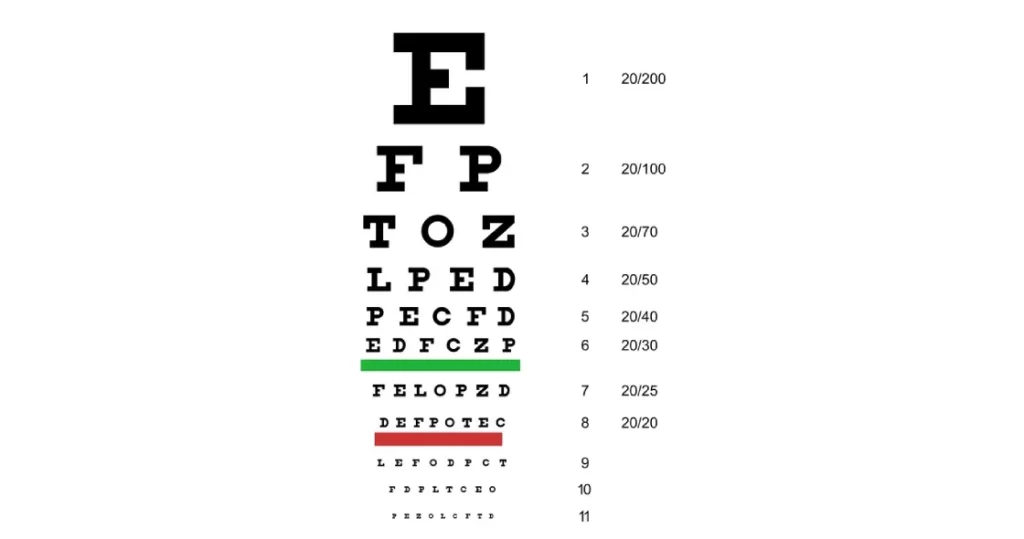
20/20 vision is a term used to express normal visual acuity (the clarity or sharpness of vision) measured at a distance of 20 feet. If you have 20/20 vision, you can see clearly at 20 feet what should normally be seen at that distance. If you have 20/100 vision, it means that you must be as close as 20 feet to see what a person with normal vision can see at 100 feet24. Because visual acuity is so easily measured, it is often used as a primary eligibility criterion. The visual acuity scale is not truncated at 20/20. 20/20 is a reference standard; it is not perfect vision. Snellen chose this standard so that all healthy young adults exceed it. This range allows reading of newsprint (1 M) at 80 to 160 cm. Since normal reading is at about 40 cm, there is a very comfortable reserve. “Normal” visual acuity for healthy eyes is one or two lines better than 20/20. In population samples the average acuity does not drop to the 20/20 level until age 60 or 70. As previously discussed, the 20/20 reference standard does not refer to the average acuity of American eyes, just as the US standard foot is defined independently of the “normal” length of American feet25. The significance of the 20/20 (1.0) standard can best be thought of as the “lower limit of normal” or as a screening cut-off. When used as a screening test, we are satisfied when subjects reach this level and feel no need for further investigation, even though the average visual acuity of healthy eyes is 20/16 (1.25) or 20/12
Teller Acuity Cards
Cards Are Effective in Detecting Amblyopia Detection of amblyopia in infants and toddlers is difficult because the current clinical standard for this age group, fixation preference, is inaccurate. Although grating acuity represents an alternative, studies of preschoolers and schoolchildren report that it is not equivalent to the gold standard optotype acuity. Here, we examine whether the Teller Acuity Cards (TAC) can detect amblyopia effectively by testing children old enough (7.8 ± 3.6 years) to complete optotype acuity testing.
What is ETDRS?
ETDRS stands for Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy Study. The first ETDRS trial was a multisite, randomized clinical trial designed to evaluate argon laser photocoagulation and aspirin treatment in the management of patients with early proliferative diabetic retinopathy. A total of 3,711 patients were recruited to be followed for a minimum of 4 years to provide long-term information on the risks and benefits of the treatments under study. Foregoing the traditional Snellen optotypes, which were at that time considered standard, better charts were needed for more accurate results. The ETDRS study introduced three new visual acuity charts, the “Original Series” with follow-up studies on those charts resulting in an additional “2000 Revised Series” which have a different letter arrangement for more homogeneous results. Both the original and revised series charts use Sloan letters. A variety of other optotypes are accepted worldwide. ETDRS equipment and testing have evolved into what is considered the gold standard of current-day clinical trials involving vision testing.